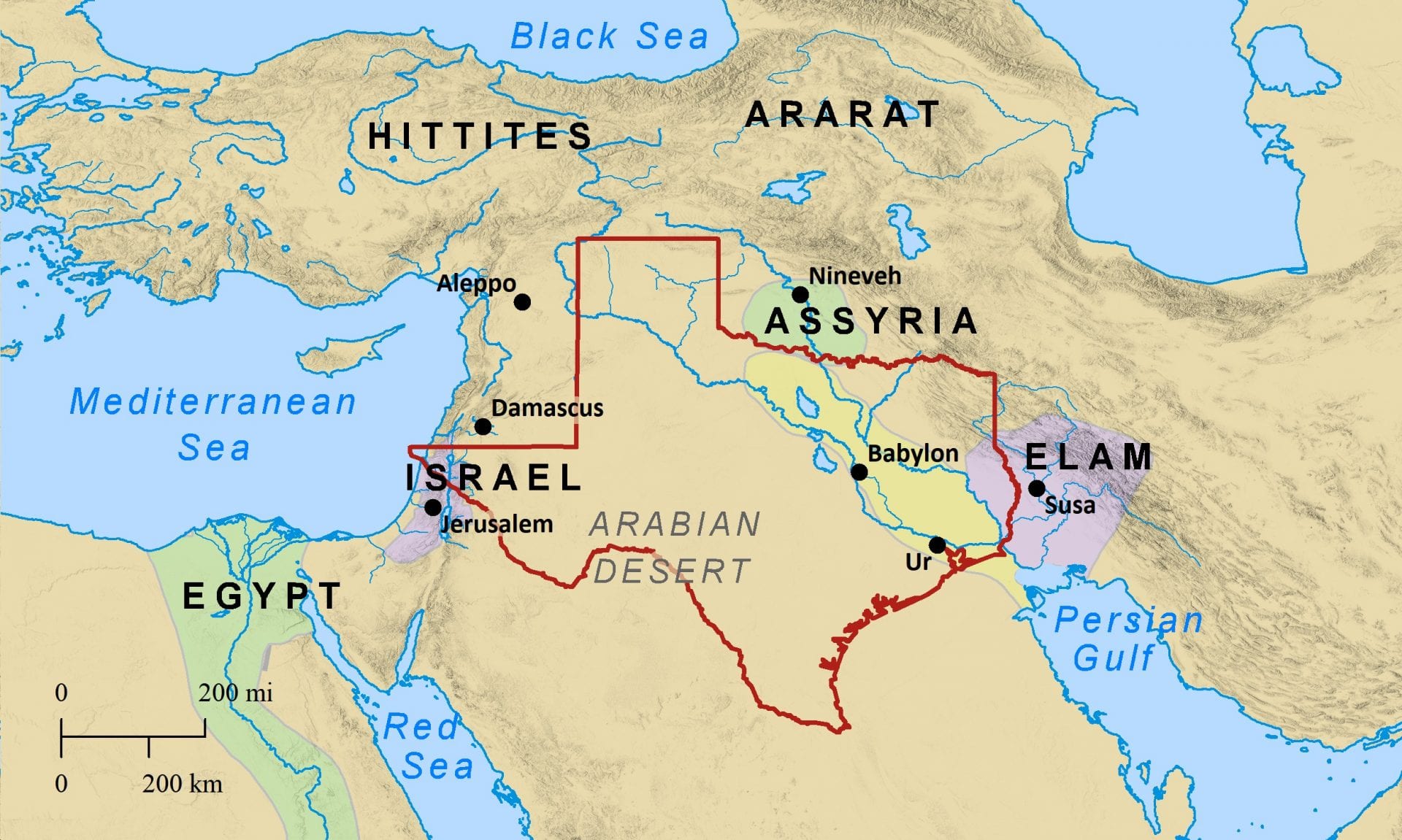
The Bible is a sacred text that has shaped the beliefs, values, and practices of countless individuals and communities throughout history. It contains a rich tapestry of narratives, teachings, and wisdom that provide guidance and inspiration for millions. To fully appreciate the depth and meaning of the biblical text, it is essential to understand the role of geography in shaping the context in which these stories unfold.
Geography played a crucial role in the lives of the people of the ancient Near East, and it heavily influenced the events and teachings depicted in the Bible. The physical features of the land, such as mountains, rivers, deserts, and seas, shaped the ways in which people lived, their interactions with neighboring communities, and the challenges they faced.
For example, the Israelites’ journey from Egypt to the Promised Land is a central theme in the Old Testament. The rugged terrain, vast deserts, and formidable obstacles they encountered along the way, such as the Red Sea and the Jordan River, not only tested their faith but also demonstrated the divine intervention and guidance they received. Understanding the geography of this region helps us appreciate the significance of their journey and the symbolism associated with crossing boundaries and entering a new land of promise.
Geography also played a vital role in the agricultural practices and livelihoods of the biblical world. The fertile valleys and plains of ancient Mesopotamia and the coastal regions of Canaan facilitated the growth of crops and supported prosperous agricultural societies. The references to “a land flowing with milk and honey” in the Bible reflect the abundance and fertility associated with specific geographic areas.
Moreover, the geography of the land shaped the geopolitical dynamics of the ancient world. The strategic location of the land of Israel, situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, made it a desirable and contested territory. The biblical narratives often depict the struggles between neighboring nations and empires vying for control over this region, highlighting the geopolitical significance of the land.
Understanding the geography of the Bible also provides insights into the cultural and religious practices of the time. The topography influenced the worship of ancient Israel, as high places and mountaintops were often associated with sacred spaces and encounters with the divine. For instance, Mount Sinai, where Moses received the Ten Commandments, and Mount Carmel, where Elijah confronted the prophets of Baal, are notable examples of the significant role of geography in religious experiences.
Furthermore, geographical references in the Bible help situate the narratives in specific locations and create a sense of authenticity. The mention of cities such as Jerusalem, Jericho, Bethlehem, and Nineveh helps readers visualize the settings and contextualize the events described. It allows readers to connect the stories to real places, making them more relatable and tangible.
Studying the geography of the Bible enhances our understanding of the context in which the scriptures were written and the challenges faced by the people of that time. It provides a lens through which we can interpret the intentions of the authors, the symbolism embedded in the narratives, and the cultural and historical influences on the text.
In conclusion,
geography played a pivotal role in the biblical world and holds significant importance in understanding the context of scripture. The physical features of the land, the geopolitical dynamics, and the cultural practices influenced the events, teachings, and experiences depicted in the Bible. Exploring the geography of the biblical world deepens our appreciation for the narratives, enhances our interpretation of the text, and enriches our understanding of the profound impact of the scriptures on human history and spirituality.
Help keep your school safe with advanced school vape detectors that monitor indoor air quality and promote a healthy learning environment. A proactive step for institutions that care about student well-being and discipline.
